Stoma stenosis is one of the common complications. Colostomy stenosis occurs in 2-15% of patients. Colostomy stenosis not only affects the difficulty of stoma defecation but also excrement leakage can cause stoma to the surrounding skin. The separation of skin and mucous membranes and narrow stoma not only make patients unable to carry out normal social activities but also have a great impact on patients' psychology. As medical staff and family members, they should give patients correct nursing guidance to eliminate patients' fear psychology. This article will Let me introduce how to treat and prevent stoma stenosis, let's take a look together!
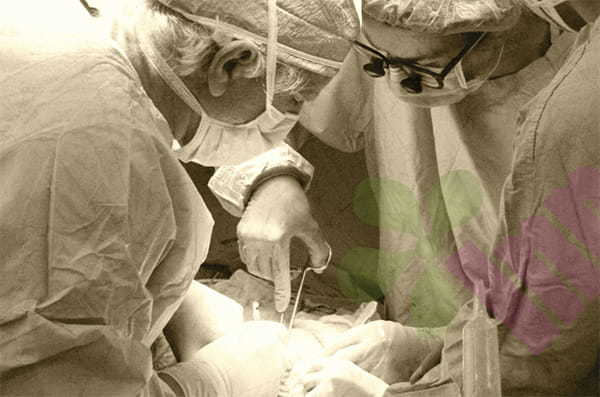
The picture below shows a stoma stenosis map:

Analysis: It can be seen that the stoma opening is very small and in a tight state, and fecal water dermatitis also appears on the surrounding skin.
What is stoma stenosis?
Stoma narrowing or tightening, manifested as a small opening of the stoma skin, difficult to see the mucous membrane or a normal skin opening of the stoma, but the tissues around the intestinal tube are tightened during the digital examination, making it difficult for fingers to enter, called stoma stenosis, which mostly occurs after surgery 8 days to several years. Stoma stenosis can lead to serious complications, such as intestinal obstruction, and stoma complications should be prevented and treated early.
What causes stoma stenosis?
With the shrinkage of the granulation tissue scar, the original size of the stoma gradually narrowed and continued to aggravate.
1. Intestinal tube length: Insufficient mobilization of the intestinal tube and insufficient length of the everted intestinal tube lead to a too short intestinal tube of the stoma, which produces traction force and causes retraction of the intestinal stoma.
2. Mucosa suture: caused by the insecure fixation of the stoma suture or the premature detachment of the suture.
3. Abdominal wall opening: The incision on the abdominal wall of the stoma is too large, which is larger than the diameter of the intestinal tube. After the edema of the intestinal mucosa subsides, the intestinal tube will become thinner, which will easily cause the retraction of the stoma.
4. Support rod: For patients with loop stoma, the stoma support rod is displaced, the intestine is not firmly fixed, or the stoma support rod is removed prematurely, resulting in retraction of the stoma.
5. Rapid weight gain: After the operation, the patient gained too much weight, and the abdominal fat around the stoma was too thick, which caused the stoma to collapse.
6. Tumor: The malignant tumor secondary to the patient's intestine grows rapidly, affecting the entire intestine and causing stoma retraction.
7. Complications: In the early stage, it is mostly due to ischemia and necrosis of the intestinal mucosa, and the intestinal tube retracts to the outside of the fascia or into the abdominal cavity after the intestinal mucosa is shed. Retraction or invagination of the enterostomy.
How to determine whether there is stenosis?
Generally, if the circumference of the stoma is ≤ the anterior segment of the little finger (the patient himself) and the patient has difficulty in defecation, it can be considered stenosis.
Mild stenosis: Those who defecate with difficulty but are still able to defecate.
Moderate stenosis: It is difficult to defecate, and it is necessary to use manual pressure on the abdomen or use drugs to assist defecation.
Severe stenosis: Difficulty in defecation, which is ineffective even with hand pressure or medicine, often accompanied by abdominal pain, abdominal distension, and even incomplete intestinal obstruction.
How to care for and prevent it?
① Surgical treatment is the best way to improve enterostomy stricture.
② Non-surgical care can regularly expand the stoma, which can start one week after the operation.
1-2 weeks after the operation, use the index finger to wear gloves and apply lubricating oil. Insert the stoma slowly until the second segment of the index finger can be inserted (the insertion depth is 3-4cm). The finger should not be rotated during insertion to avoid mucosal bleeding. 5 ~10 minutes once, 1~2 times a week.
Patients with stenosis should dilate the anus every day, starting with the little finger, usually 2 to 3 times a day, if there is pain and discomfort, take a deep breath. After gradually getting better, use the index finger and middle finger instead, and insist on 3~6 times a month, so that the diameter of the stoma is 2~2.5cm.
③Keep a regular diet, avoid eating spicy, raw, cold, and hard irritating food, and try to focus on soft food that is easy to digest.
④Regular follow-up visits, if there is any abnormality in exhaust and defecation, please go to the local stoma clinic for professional help in time.
For more information on Innomed® ostomy attachment, refer to the previous articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; we will serve you wholeheartedly.
At Longterm Medical, we transform this data by innovating and developing products that make life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia
Date: December 30, 2022

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体