In daily life, it is sometimes unavoidable to get bruised, broken, cut, burned, or scalded. If a serious wound or limb injury is not treated promptly, it may cause complications such as infection or functional impairment within a few hours. Proper treatment can reduce the occurrence of complications. Today, let's learn some common sense of trauma first aid. Come and learn it!
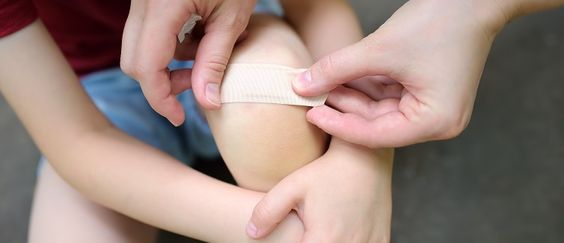
How do you treat abrasions, cuts, and burns?
Superficial wound management:
For minor abrasions or superficial cuts, the first step is to clean the wound to reduce the risk of infection. If conditions permit, the ideal cleaning solution is saline, which can effectively remove dirt and bacteria from the surface of the wound. However, in emergency situations, clean tap water can also be used as an alternative. After cleaning, gently apply a disinfectant such as iodine to the wound. This step can further kill residual bacteria. Next, cover the wound with a hydrocolloid bandage to protect it from external contamination. Every one to two days, the bandage should be gently removed to observe the healing of the wound, and then disinfected and bandaged again.
Deep wound treatment:
For more serious wounds, such as deep cuts or heavy bleeding, apply firm pressure with sterile gauze to control bleeding. If the bleeding does not stop after more than five minutes of pressure, seek medical help immediately. If the wound is caused by an animal or human bite, it should be considered an emergency regardless of the amount of bleeding, as bites can be accompanied by bacterial or viral infections. Deep wounds and wounds pierced by sharp objects such as glass or metal also require immediate medical attention. If you lose pain in the wound area, it may be a sign of nerve damage; if the injured area is limited in movement, it may involve tendon or bone damage; if redness, swelling, heat, pain and pus appear, these are clear signs of infection, and these situations should not be ignored and require medical attention as soon as possible.
Treatment of burns and scalds:
The treatment of burns and scalds requires different measures according to the degree and type of burns. For mild burns, such as reddish skin or small blisters, the wound can be immediately rinsed with plenty of cold water to reduce the surface temperature of the skin and relieve pain. The rinsing time should last for 10 to 30 minutes, and then the wound should be gently wrapped with a clean towel or clothing to avoid friction and infection. For more serious burns, such as large blisters, peeling or even charred skin, the patient should be sent to the hospital for professional treatment immediately. During the medical treatment, the wound can be covered with clean clothing or sheets to keep the wound clean and reduce the risk of infection.

Do I need a tetanus shot?
Long and deep wounds, especially those caused by nails, wood thorns and other contaminants, are very susceptible to infection with tetanus bacteria. Once this bacterium invades the body, it can cause severe tetanus disease, affect the central nervous system, cause muscle spasms and stiffness, and even endanger life. Therefore, for such wounds, it is recommended to go to the emergency surgery department immediately to receive a preventive injection of tetanus antitoxin.
For more information on Innomed® Hydrogel Dressing, Refer to the Previous Articles. If you have customized needs, you are welcome to contact us; You Wholeheartedly. At longterm medical, we transform this data by Innovating and Developing Products that Make Life easier for those who need loving care.
Editor: kiki Jia

 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体








